|
Chemicals
 Acetone
Acetone
Acetone
CAS number 67-64-1
![Acetone CAS number [67-64-1]](api%20images1/Acetone.jpg)
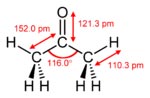

Identifiers
CAS number [67-64-1]
RTECS number AL31500000
SMILES CC(=O)C InChI
1/C3H6O/c1-3(2)4/h1-2H3
ChemSpider ID 175
Properties
Molecular Weight: 58.08
Molecular formula C3H6O
Molar mass 58.08 g mol−1
Appearance Colorless liquid
Density 0.79 g/cm3
Melting point −94.9 °C, 178 K, -139 °F
Boiling point 56.53 °C, 330 K, 134 °F
Solubility in water miscible
Viscosity 0.32 cP at 20 °C
Structure
Molecular shape trigonal planar at C=O
Dipole moment 2.91 D
Hazards
MSDS External MSDS
EU classification Flammable F
Irritant Xi
R-phrases R11, R36, R66, R67
S-phrases (S2), S9, S16, S26
NFPA 704 310
Flash point -17 °C
Autoignition
temperature 465 °C
Explosive limits 4.0–57.0
Related compounds
Related solvents Water
Ethanol
Isopropanol
Toluene
Supplementary data page
Structure and
properties n, εr, etc.
Thermodynamic
data Phase behaviour
Solid, liquid, gas
Spectral data UV, IR, NMR, MS
Product Overview
Acetone is one of the most widely used industrial solvents and is
increasingly used as a chemical intermediate. See Product Uses.
Acetone is low in toxicity. It is a natural product of our body’s
metabolism. See Health Information.
Acetone does not cause adverse health or environmental effects at
levels typically found in the workplace or environment.
Acetone is extremely flammable with a high vapor pressure; use only
with good ventilation and avoid all ignition sources. See Physical
Hazard Information.
Product Description
Acetone is a clear, colorless, low-boiling, flammable and volatile
liquid characterized by rapid evaporation and a faintly aromatic,
sweetish odor.
It readily mixes with most organic solvents and mixes completely
with water. However, compatibility should be checked prior to mixing
with other solvents or materials.
Product Uses
Roughly 75% of the available acetone is used to produce other
chemicals,4 and 12% is used as a solvent. Applications range from
surface coatings, films and adhesives to cleaning fluids and
pharmaceutical applications. Other consumer and commercial
applications include:
* Lacquers for automotive/furniture finishes
* Cellulose acetate films and fibers
* Photographic films and plates casting
* Coatings and inks
* Resin thinners and clean-up operations
* General purpose cements
* Degreasing and degumming agents
* Paint, varnish, lacquer strippers
* Nail polish removers
* Various cosmetic product
Health Information
Acetone has been studied extensively and is generally recognized to
have low acute and chronic toxicity if ingested and/or breathed.
Breathing high concentrations (around 9200 ppm) in the air caused
irritation of the throat in humans in as little as 5 minutes.
Breathing concentrations of 1000 ppm caused irritation of the eye
and throat in less than 1 hour; however, breathing 500 ppm of
acetone in the air caused no symptoms of irritation in humans even
after 2 hours of exposure. Acetone is not currently regarded as a
carcinogen, a mutagenic chemical or a concern for chronic
neurotoxicity effects
Environmental Information
Acetone is not expected to present a threat to the environment
because of its low toxicity, high volatility and complete solubility
in water. The intent, however, is to minimize any exposure to the
environment from manufacturing and use activities.
Firefighting guidelines should be followed closely. Additional
information can be found on the Safety Data Sheet (SDS).
Physical Hazard Information
Acetone is a highly flammable material in both the liquid and vapor
forms, has a relatively high vapor pressure, and should be handled
only with adequate ventilation and in areas where ignition sources
have been removed (e.g. matches and unprotected light switches).
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 |



