|
Chemicals
 Phenylacetic
acid Phenylacetic
acid
Phenylacetic acid
CAS number
[103-82-2]
IUPAC name
Phenylacetic acid
MOL WT. 136.15
H.S. CODE : 2916.33
 Identifiers Identifiers
CAS number [103-82-2]
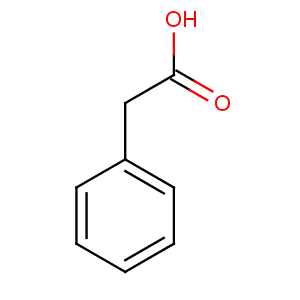
SMILES c1ccccc1CC(=O)O
Properties
Molecular formula C8H8O2
Molar mass 136.15 g/mol
Density 1.0809 g/cm3
Melting point 76-77 °C
Boiling point 265.5 °C
Hazards
MSDS External MSDS
Phenylacetic acid (abr. PAA and synonyms are: α-toluic acid,
benzeneacetic acid, alpha tolylic acid, 2-phenylacetic acid) is an
organic compound containing a phenyl functional group and an acetic
acid functional group.
Because it is used in the illicit production of phenylacetone (used
in the manufacture of meth/amphetamines), it is subject to controls
in the United States.
Physical data
Appearance: white crystals with a honey-like odour
Melting point: 77 C
Boiling point: 265 C
Vapour density:
Vapour pressure: 1 mm Hg at 97 C
Density (g/cm3): 1.228
Flash point: 190
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Phenylacetic acid ≥ 99%
Stability
Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents.
Toxicology
Harmful by ingestion, inhalation or through skin contact. Severe eye
irritant. Skin and respiratory irritant. May act as a teratogen.
Oral rat LD50 2250 mg/Kg
Toxicity data
(The meaning of any abbreviations which appear in this section is
given here.)
ORL-RAT LD50 2250 mg kg-1
ORL-GPG LD50 2250 mg kg-1
IPN-RAT LD50 1600 mg kg-1
Risk phrases
(The meaning of any risk phrases which appear in this section is
given here.)
R20 R21 R22 R36 R37 R38.
Personal protection
Safety glasses. Adequate ventilation.
NFPA
RATINGS Health: 1 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 0 FLASH POINT
190 C
STABILITY Stable under ordinary
conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Phenylacetic acid is a white crystals
with a disagreeable odor; boiling point 262 C; soluble in alcohol
and ether. It serves as an ingredient in perfume to provide
honey-like odor. It is found as a moiety in some alkaloids and plant
hormones. It is formed as catabolite of phenylalanine. In toluic
acid name system, phenylacetic acid is alpha-toluic acid which one
of the hydrogen atoms in the methyl group has been substituted
instead of the substitution in the benzene ring. Substituted
phenylacetic acid molecule at alpha position and phenylacetate
esters can serve as a drug with a wide variety of effects including
anticholinergic, muscarinic antagonist, antidote to cholinesterase
inhibitors or toxins, cycloplegic and mydriatic. Phenylacetic acid
is used to prepare a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug like
diclofenac. It is used the manufacture of penicillin. Mandelic Acid,
phenylglycollic acid, can be produced from phenylchloracetic acid.
APPEARANCE
White to
creamy flaky powder PURITY (GLC)
99.0% min
MELTING POINT 76 - 78 C
WATER 1.0% max
TRANSPORTATION
PACKING 25kgs in bag
HAZARD CLASS
UN NO.
REMARKS
Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases:
36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 22/24/25
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 |



