|
Chemicals
 Piperidine
Piperidine
Piperidine
CAS number 110-89-4
General
Synonyms: hexahydropyridine, pentamethyleneimine, azacyclohexane,
cyclopentimine, cypentil, hexazane,
Molecular formula: C5H11N
CAS No: 110-89-4
EINECS No: 203-813-0
Annex I Index No: 613-027-00-3
 Physical
data Physical
data
Appearance: colourless liquid with the odour of pepper
Melting point: -11 C
Boiling point: 106 C
Vapour density: 3 (air = 1)
Vapour pressure: 40 mm Hg at 20 C
Density (g cm-3): 0.86
Flash point: 16 C (closed cup)
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility: soluble
Stability
Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents,
strong acids, organic acids, water. Vapours may flow along surfaces
to a distant source of ignition.
Toxicology
Poison. May be fatal if inhaled or swallowed. Severe irritant. Skin
contact may cause severe irritation or burns. Contact with the eyes
may lead to permanent damage.
Toxicity data
ORL-RAT LD50 400 mg kg-1
IPR-MUS LD50 50 mg kg-1
SKN-RBT LD50 320 mg kg-1
ORL-MUS LD50 30 mg kg-1
ORL-RBT LD50 145 mg kg-1
Risk phrases
R11 R23 R24 R34. (Note: The risk phrases here are those given by
Annex I. Annex I does not specify R22 or R25, but this material is
clearly harmful if swallowed so should be treated as though R22 were
included.]
Personal protection
Safety glasses, gloves, good ventilation. Remove sources of ignition
from the working area.
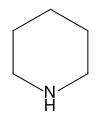
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula
(CH2)5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring
containing five methylene units and one nitrogen atom. It is a
colorless fuming liquid with an odor described as ammoniacal,
pepper-likethe name comes from the genus name Piper, which is the
Latin word for pepper. Piperidine is a widely used building block
and chemical reagent in the synthesis of organic compounds,
including pharmaceuticals.
a colorless, liquid hydrocarbon, (CH)NH, found in many alkaloids and
obtained by reducing pyridine or by treating piperine with alkali:
used in making rubber, oils, fuels, etc.
Production
Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of
pyridine, usually over a molybdenum sulfide catalyst
Production
Industrially, piperidine is produced by the hydrogenation of
pyridine, usually over a molybdenum sulfide catalyst
Uses
Piperidine is used as a solvent and as a base. The same is true for
certain derivatives: N-formylpiperidine is a polar aprotic solvent
with better hydrocarbon solubility than other amide solvents, and
2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine is highly sterically hindered base,
useful because of its low nucleophilicity and high solubility in
organic solvents.
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 |



