|
Chemicals
 Pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine
CAS number 90-82-4
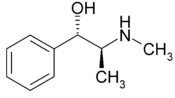 Systematic
(IUPAC) name Systematic
(IUPAC) name
(1S,2S)-2-methylamino-1-phenylpropan-1-ol
Identifiers
CAS number 90-82-4
ATC code R01BA02
PubChem 7028
DrugBank APRD00634
ChemSpider 6761
Chemical data
Formula C10H15NO
Mol. mass 165.23
Pharmacokinetic data
Bioavailability unknown
Metabolism hepatic (10–30%)
Half life 9–16 hours
Excretion 70-90% renal
Pseudoephedrine is a decongestant that shrinks blood vessels in
the nasal passages. Dilated blood vessels can cause nasal congestion
(stuffy nose).
Pseudoephedrine is used to treat nasal and sinus congestion, or
congestion of the tubes that drain fluid from your inner ears,
called the eustachian (yoo-STAY-shun) tubes.
Important information about pseudoephedrine
Always ask a doctor before giving a cough or cold medicine to a
child. Death can occur from the misuse of cough and cold medicines
in very young children. Do not use any other over-the-counter cough
or cold medication without first asking your doctor or pharmacist.
If you take certain products together you may accidentally take too
much of a certain drug. Read the label of any other medicine you are
using to see if it contains pseudoephedrine. Do not use a cough or
cold medicine if you have used an MAO inhibitor such as
isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), rasagiline (Azilect),
selegiline (Eldepryl, Emsam), or tranylcypromine (Parnate) within
the past 14 days. Serious, life-threatening side effects can occur
if you take cough or cold medicine before the MAO inhibitor has
cleared from your body.
Pseudoephedrineis a sympathomimetic amine commonly used as a
decongestant. The salts pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and
pseudoephedrine sulfate are found in many over-the-counter
preparations either as single-ingredient preparations, or more
commonly in combination with antihistamines, paracetamol
(acetaminophen) and/or ibuprofen. Sudafed is a trademark for a
common brand which contains pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, though
Sudafed PE does not. Cirrus contains Pseudoephedrine in conjunction
with Cetirizine (an antihistamine).The advantage of oral
pseudoephedrine over topical nasal preparations, such as
oxymetazoline, is that it does not cause rebound congestion
(rhinitis medicamentosa); however, it is more likely to cause
adverse effects including hypertension.
Clinical uses
Indications
Pseudoephedrine is indicated for the treatment of:
* nasal congestion
* sinus congestion
* Eustachian tube congestion.
Pseudoephedrine is also indicated for vasomotor rhinitis, and as an
adjunct to other agents in the optimum treatment of allergic
rhinitis, croup, sinusitis, otitis media, and
tracheobronchitisPseudoephedrine is also used as first-line therapy
of priapism. Erection is largely a parasympathetic response, so the
sympathetic action of pseudoephedrine may serve to relieve this
condition.
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 |



