|
|
HOME >>
Agro
Chemicals >> Ethyl Alcohol

Ethyl Alcohol
CAS No: 64-17-5
General
Synonyms: ethanol, grain alcohol, fermentation alcohol, alcohol,
methylcarbinol, absolute alcohol, absolute ethanol, anhydrous alcohol,
alcohol dehydrated, algrain, anhydrol, Cologne spirit, duplicating fluid
100C, ethyl hydrate, ethyl hydroxide, jaysol, jaysol s, molasses alcohol,
potato alcohol, sekundasprit, spirits of wine, spirit, synasol, tecsol
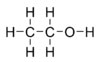
Molecular C2H5OH
CAS No: 64-17-5
EC No: 200-578-6
Annex I Index No: 603-002-00-5
Physical data
Appearance: colourless liquid
Melting point: -114 C
Boiling point: 78 C
Specific gravity: 0.789
Vapour pressure: 1.59
Flash point: 14 C (closed cup)
Explosion limits: 3.3% - 24.5%
Autoignition temperature: 363 C
Water solubility: miscible in all proportions
Stability
Stable. Substances to be avoided include strong oxidizing agents, peroxides,
acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, alkali metals, ammonia, moisture.
Forms explosive mixtures with air. Hygroscopic.
Toxicology
Causes skin and eye irritation. Ingestion can cause nausea, vomitting and
inebriation; chronic use can cause serious liver damage. Note that
"absolute" alcohol, which is close to 100% ethanol, may nevertheless contain
traces of 2-propanol, together with methanol or benzene.
The latter two are very toxic, while "denatured" alcohol has substances
added to it which make it unpleasant and possibly hazardous to consume.
Typical OEL 1000 mg/m3.
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking
alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive
drug, best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages and in
modern thermometers. Ethanol is one of the oldest recreational drugs. In
common usage, it is often referred to simply as alcohol or spirits.
Ethanol is a straight-chain alcohol, and its molecular formula is C2H5OH.
Its empirical formula is C2H6O.
An alternative notation is CH3-CH2-OH, which indicates that the carbon of a
methyl group (CH3-) is attached to the carbon of a methylene group (-CH2-),
which is attached to the oxygen of a hydroxyl group (-OH). It is a
constitutional isomer of dimethyl ether.
Physical properties
Ethanol burning with its spectrum depicted
Ethanol is a volatile, colorless liquid that has a strong characteristic
odor. It burns with a smokeless blue flame that is not always visible in
normal light.
The physical properties of ethanol stem primarily from the presence of its
hydroxyl group and the shortness of its carbon chain.
Ethanolís hydroxyl group is able to participate in hydrogen bonding,
rendering it more viscous and less volatile than less polar organic
compounds of similar molecular weight.

|


