|
|
HOME >>
API >>
API List1 >>
Budesonide

CAS number 51333-22-3

ATC code A07EA06 D07AC09, R01AD05, R03BA02
structural formula is:
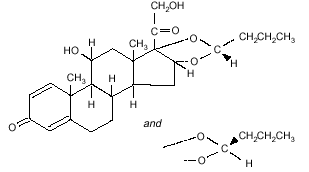
Formula C25H34O6
Mol. mass 430.534 g/mol
SMILES eMolecules & PubChem
Its partition coefficient between octanol and water at pH 5 is 1.6 x 10.3
Pharmacokinetic data
Bioavailability 100% (but large first pass effect)
Protein binding 85-90%
Metabolism Hepatic CYP3A4
Half life 2.0-3.6 hours
Excretion Renal, Faecal
Chemical data
Budesonide is designated chemically as
(RS)-11-beta, 16-alpha, 17, 21-tetrahydroxypregna-1,
4-diene-3,20-dione cyclic 16, 17-acetal with butyraldehyde.
Budesonide is provided as the mixture of two epimers (22R and 22S).
The empirical formula of budesonide is C25H34O6 and its molecular weight is
430.5.
Budesonide is a white to off-white, odorless powder that is practically
insoluble in water and in heptane,
sparingly soluble in ethanol, and freely soluble in chloroform.
GENERIC NAME: Budesonide
DRUG CLASS AND MECHANISM: Budesonide is a man-made glucocorticoid
steroid related to the naturally-occurring hormone, cortisol or
hydrocortisone which is produced in the adrenal glands. It is used for
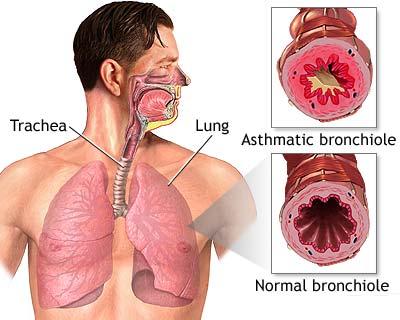
treating asthma by inhalation. Glucocorticoid steroids such as cortisol or
budesonide have potent anti-inflammatory actions that reduces inflammation
and hyper-reactivity (spasm) of the airways caused by asthma. When used as
an inhaler, the budesonide goes directly to the inner lining of the inflamed
airways to exert its effects. Only 39% of an inhaled dose of budesonide is
absorbed into the body, and the absorbed budesonide contributes little to
the effects on the airways.
GENERIC AVAILABLE: No
PRESCRIPTION: Yes
PREPARATIONS:
Pulmicort Turbuhaler 200 mcg: each 200 mcg actuation delivers 160 mcg of
budesonide.
Pulmicort Respules, 0.25 mg/2ml, 0.5 mg/2ml suspension, and 1 mg/2ml
STORAGE: Budesonide should be stored at room temperature, 20-25 C
(68-77 F).
PRESCRIBED FOR: The budesonide inhaler is used for the control of asthma in
persons requiring continuous, prolonged treatment. Such patients may include
those with frequent asthmatic episodes requiring bronchodilators, for
example, albuterol (Ventolin) or those with asthmatic episodes at night.

DOSING: Budesonide is used to prevent asthmatic attacks and should
not be used to treat an acute attack of asthma. The Turbuhaler is used for
individuals six years of age or older. Effects can be seen within 24 hours,
but maximum effects may not be seen for 1-2 weeks or longer. Doses vary
widely. Adults usually receive 1 to 4 actuations (puffs) twice daily.
Children usually receive 1 to 2 puffs twice daily. For those with mild
asthma, treatment once daily may be sufficient.
Pulmicort Respules are used for individuals 12 months to eight years of age.
Effects are seen in 2 to 8 days, but maximum effects may not be seen for up
to 4 to 6 weeks. Pulmicort Respules are used with a jet nebulizer. They
usually are taken as one or two doses for a total of 0.5-1 mg daily.
DRUG INTERACTIONS: Ketoconazole (Nizoral, Extina, Xolegel, Kuric)
increases the concentrations in blood of budesonide, and this may lead to an
increase in the side effects of budesonide. No drug interactions have been
described with inhaled budesonide.
PREGNANCY: When given orally to animals, glucocorticoid steroids
similar to budesonide have been shown to cause fetal abnormalities. Studies
of pregnant women using inhaled budesonide during early pregnancy, however,
do not show an increase in the rate of fetal abnormalities. Nevertheless,
since these studies cannot exclude the possibility of rare effects on the
fetus, inhaled budesonide should be used with caution during pregnancy.
NURSING MOTHERS: It is not known if budesonide is secreted in breast
milk. Other medications similar to budesonide are indeed secreted in breast
milk. It is not known whether the small amounts that may appear in breast
milk have effects on the infant.
SIDE EFFECTS: The most commonly noted side effects associated with
inhaled budesonide are mild cough or wheezing; these effects may be
minimized by using a bronchodilator inhaler, for example, albuterol (Ventolin),
prior to the budesonide. Oral candidiasis or thrush (a fungal infection of
the throat) may occur in 1 in 25 persons who use budesonide without a spacer
device on the inhaler. The risk is even higher with large doses but is less
in children than in adults. Hoarseness or sore throat also may occur in 1 in
10 persons. Using a spacer device on the inhaler and washing one's mouth out
with water following each use reduces the risk of both thrush and
hoarseness. Less commonly, alterations in voice may occur.
High doses of inhaled glucocorticoid steroids may decrease the formation and
increase the breakdown of bone leading to weakened bones and ultimately
osteoporosis and fractures. High doses may suppress the body's ability to
make its own natural glucocorticoid in the adrenal gland. It is possible
that these effects are shared by budesonide. People with suppression of
their adrenal glands (which can be tested for by the doctor) need increased
amounts of glucocorticoid steroids orally or intravenously during periods of
high physical stress, for example, during infections, to prevent serious
illness and shock.
Hypersensitivity reactions such as anaphylaxis, rash, contact dermatitis,
itching, angioedema, and bronchospasm have been reported with use of inhaled
budesonide. Use should be discontinued if such reactions occur.
 
|