|
HOME >>
API >>
API List1 >>
Atorvastatin Calcium

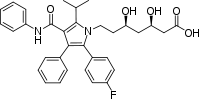
Atorvastatin Calcium

CAS number
134523-00-5
ATC code C10AA05
PubChem CID 60823
DrugBank APRD00055
ChemSpider 54810
UNII A0JWA85V8F
Chemical data
Formula C33H35FN2O5
Mol. mass 558.64
SMILES eMolecules & PubChem
Pharmacokinetic data
Bioavailability 12%
Metabolism Hepatic - CYP3A4
Half-life 14 h
Excretion Bile
Therapeutic considerations
Pregnancy cat. D(AU) X(US)
Legal status Prescription Only (S4) (AU) POM (UK) ℞-only (US)
Routes oralWhat is atorvastatin?
Atorvastatin is a cholesterol-lowering medication that blocks the production of cholesterol (a type of fat) in the body. Atorvastatin reduces low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol and total cholesterol in the blood. Lowering your cholesterol can help prevent heart disease and hardening of the arteries, conditions that can lead to heart attack, stroke, and vascular disease.
Atorvastatin is used to treat high cholesterol. Atorvastatin is also used to lower the risk of stroke, heart attack, or other heart complications in people with coronary heart disease or type 2 diabetes.
Important information about atorvastatin
In rare cases, atorvastatin can cause a condition that results in the breakdown of skeletal muscle tissue. This condition can lead to kidney failure. Call your doctor at once if you have unexplained muscle pain or tenderness, muscle weakness, fever or flu symptoms, and dark colored urine.
This medication can cause birth defects in an unborn baby. Do not use if you are pregnant. Use an effective form of birth control, and tell your doctor if you become pregnant during treatment. Do not take atorvastatin if you are pregnant or breast-feeding, or if you have liver disease.
Before taking atorvastatin, tell your doctor if you have diabetes, underactive thyroid, kidney disease, a muscle disorder, or a history of liver disease.
Avoid eating foods that are high in fat or cholesterol. Atorvastatin will not be as effective in lowering your cholesterol if you do not follow a cholesterol-lowering diet plan.
Avoid drinking alcohol while taking atorvastatin. Alcohol can raise triglyceride levels, and may also damage your liver while you are taking this medication.
There are many other drugs that can interact with atorvastatin. Tell your doctor about all the prescription and over-the-counter medications you use. This includes vitamins, minerals, herbal products, and drugs prescribed by other doctors. Do not start using a new medication without telling your doctor.
Before taking atorvastatin
Do not use this medication if you are allergic to atorvastatin, if you are pregnant or breast-feeding, or if you have liver disease.
If you have certain conditions, you may need a dose adjustment or special tests to safely take this medication. Before taking atorvastatin, tell your doctor if you have:
-
diabetes;
-
underactive thyroid;
- kidney disease;
- a history of liver disease; or
-
a muscle disorder.
FDA pregnancy category X. This medication can cause birth defects. Do not use atorvastatin if you are pregnant. Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant during treatment. Use an effective form of birth control while you are using this medication. It is not known whether atorvastatin passes into breast milk or if it could harm a nursing baby. Do not take this medication without telling your doctor if you are breast-feeding a baby. Atorvastatin is not for use in children younger than 10 years of age.
How should I take atorvastatin?
Take atorvastatin exactly as it was prescribed for you. Do not take the medication in larger amounts, or take it for longer than recommended by your doctor. Follow the directions on your prescription label.
Take atorvastatin with a full glass of water. This medicine can be taken with or without food.
Atorvastatin is usually taken once a day. Try to take your dose at the same time each day. Follow your doctor's instructions.
To be sure this medication is helping your condition, your blood will need to be tested on a regular basis. Your liver function may also need to be tested. Do not miss any scheduled appointments.
In rare cases, atorvastatin can cause a condition that results in the breakdown of skeletal muscle tissue. This condition can lead to kidney failure. Call your doctor at once if you have unexplained muscle pain or tenderness, muscle weakness, fever or flu symptoms, and dark colored urine.
Atorvastatin is only part of a complete program of treatment that also includes diet, exercise, and weight control. Follow your diet, medication, and exercise routines very closely.
You may need to take this medication on a long-term basis for the treatment of high cholesterol.
Store atorvastatin at room temperature, protected from moisture, heat, and light.
See also: Atorvastatin dosage in more detail
What happens if I miss a dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember. If it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and take only the next regularly scheduled dose. Do not take extra medicine to make up the missed dose.
What happens if I overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention if you think you have used too much of this medicine.
An overdose of atorvastatin is not expected to produce life-threatening symptoms.
What should I avoid while taking atorvastatin?
Avoid eating foods that are high in fat or cholesterol. Atorvastatin will not be as effective in lowering your cholesterol if you do not follow a cholesterol-lowering diet plan.
Avoid drinking alcohol while taking atorvastatin. Alcohol can raise triglyceride levels, and may also damage your liver while you are taking this medication.
Grapefruit and grapefruit juice may interact with atorvastatin and lead to potentially dangerous effects. Discuss the use of grapefruit products with your doctor. Do not increase or decrease the amount of grapefruit products in your diet without first talking to your doctor.
Atorvastatin side effects
Get emergency medical help if you have any of these signs of an allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. Stop using atorvastatin and call your doctor at once if you have any of these serious side effects:
-
muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness with fever or flu symptoms; or
-
nausea, stomach pain, low fever, loss of appetite, dark urine, clay-colored stools, jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
Less serious atorvastatin side effects may include:
-
mild nausea or stomach pain, stomach upset, heartburn;
-
constipation, bloating, gas;
-
stuffy nose; or
-
itching, skin rash; or
-
headache.
This is not a complete list of side effects and others may occur. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
See also: Atorvastatin side effects (in more detail)
Atorvastatin Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease:
Initial dose: 10 mg to 80 mg orally once a day.
The initial dosage of atorvastatin recommended for this patient in the prevention of cardiovascular disease is 10 mg to 80 mg orally once a day. Atorvastatin may be administered at any time of the day without regard for meals.
Studies have demonstrated that treatment with atorvastatin is associated with significant reductions in the risk of cardiovascular endpoints and stroke in various patient populations for both primary and secondary prevention.
For primary prevention, atorvastatin treatment was effective in hypertensive patients with normal or mildly elevated cholesterol levels as well as in patients with type II diabetes. Patients had relatively low cholesterol levels at baseline in both trials; however, treatment with atorvastatin still resulted in significant reductions in cardiovascular outcomes and stroke.
For secondary prevention, intensive lipid lowering therapy with atorvastatin 80 mg/day was associated with significant incremental clinical benefit beyond therapy with 10 mg/day in patients with stable coronary heart disease. It was also shown to significantly reduce the risk of clinical outcomes in coronary heart disease patients versus usual medical care.
Usual Adult Dose for Hyperlipidemia:
Initial dose: 10, 20 or 40 mg orally once a day. The 40 mg starting dose is recommended for patients who require a reduction in LDL-cholesterol of more than 45%.
Maintenance dose: 10 to 80 mg orally once a day.
Usual Pediatric Dose for Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia:
10 to 17 years:
10 mg per day (max dose is 20 mg per day). Adjustments should be made at intervals of 4 weeks or more.
What other drugs will affect atorvastatin?
Many drugs can interact with atorvastatin. Below is just a partial list. Tell your doctor if you are using:
-
digoxin (digitalis, Lanoxin, Lanoxicaps);
-
erythromycin (E-Mycin, E.E.S., Ery-Tab, others) or clarithromycin (Biaxin);
-
gemfibrozil (Lopid) or fenofibrate (Tricor);
-
niacin (Nicolar, Nicobid, Slo-Niacin, others);
-
an antifungal medication such as itraconazole (Sporanox), fluconazole (Diflucan), or ketoconazole (Nizoral);
-
drugs that weaken your immune system such as cancer medicine or steroids, cyclosporine (Neoral, Sandimmune, Gengraf), sirolimus (Rapamune), tacrolimus (Prograf), and others;
-
HIV or AIDS medication such as indinavir (Crixivan), nelfinavir (Viracept), ritonavir (Norvir), lopinavir-ritonavir (Kaletra), or saquinavir (Invirase, Fortovase).
This list is not complete and there may be other drugs that can interact with atorvastatin. Tell your doctor about all the prescription and over-the-counter medications you use. This includes vitamins, minerals, herbal products, and drugs prescribed by other doctors. Do not start using a new medication without telling your doctor.

Details |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|



