|
HOME >>
API >>
Codeine Phosphate Hemihydrate


|
Codeine phosphate
hemihydrate

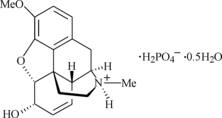
|
|
CAS No. :
41444-62-6
Molecular Formula: C18H24NO7P
Formula Weight: 397.36
Mol weight : 406.4
Chemical Name : CODEINE PHOSPHATE
Synonyms: N-METHYLNORCODEINE
HEMIHYDRATE;MORPHINE-3-METHYL ETHER HEMIHYDRATE;CODEINE
PHOSPHATE;CODEINE PHOSPHATE HEMIHYDRATE;CODEINIUM PHOSPHATE
HEMIHYDRATE;METHYLMORPHINE PHOSPHATE HEMIHYDRATE;Morphinan-6-ol,
7,8-didehydro-4,5-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methyl-,
(5.alpha.,6.alpha.)-, phosphate (salt), hydrate
(2:2:1);CODEINEPHOSPHATE,USP;Codein phosphate
hemihydrate;Codeine·phosphoric acid·0.5hydrate
CHARACTERS
Appearance: white or almost white, crystalline powder or
small, colourless crystals.
Solubility : freely soluble in water, slightly soluble in
ethanol (96 per cent). |
History
Codeine is an alkaloid found in opium and other poppy saps like
Papaver bracteatum, the Iranian poppy, in concentrations ranging
from 0.3 to 3.0 percent. While codeine can be extracted from opium,
most codeine is synthesized from morphine through the process of O-methylation.
It was first isolated in 1832 in France by Jean-Pierre Robiquet.
The effects of the Nixon War On Drugs by 1972 or so had caused
across-the-board shortages of illicit and licit opiates because of a
scarcity of natural opium, poppy straw and other sources of opium
alkaloids, and the geopolitical situation was getting less helpful
for the United States. After a large percentage of the opium and
morphine in the US National Stockpile of Strategic & Critical
Materials had to be tapped in order to ease severe shortages of
medicinal opiates—the codeine-based antitussives in particular—in
late 1973, researchers were tasked with and quickly succeeded in
finding a way to synthesize codeine and its derivatives and
precursors from scratch from petroleum or coal tar using a process
developed at the United States' National Institutes of Health.
SIDE EFFECTS
The most frequent adverse reactions include lightheadedness,
dizziness, sedation, nausea, and vomiting. These effects seem to be
more prominent in ambulatory than in non ambulatory patients, and
some of these adverse reactions may be alleviated if the patient
lies down.
Other adverse reactions include euphoria, dysphoria, constipation,
and pruritus.
Drug Abuse and Dependence
Controlled Substance: Codeine phosphate is a Schedule II narcotic.
Dependence
Although much less potent in this regard than morphine, codeine can
produce drug dependence a.d. therefore, has the potential for being
abused. Patients given 60 mg codeine every 6 hours for 2 months
usually show some tolerance and mild withdrawal symptoms.
Development of the dependent state is recognized by an increased
tolerance to the analgesic effect and the appearance of purposive
phenomena (complaints, pleas, demands, or manipulative actions)
shortly before the time of the next scheduled dose. A patient in
withdrawal should be treated in a hospital environment. Usually, it
is necessary only to provide supportive care with administration of
a tranquilizer to suppress anxiety. Severe symptoms of withdrawal
may require administration of a replacement narcotic.
INTERACTION
Carbamazepine, hydantoins, sulfinpyrazone
May result in increased risk of hepatotoxicity.
Cimetidine
Effects of codeine may be enhanced, increasing toxicity.
CNS depressants (eg, barbiturates, ethyl alcohol, other narcotics)
May result in additive CNS depressant effects and toxicity.
Tricyclic antidepressants, phenothiazines
May cause additive CNS depressant effects and toxicity.
Laboratory Test Interactions
With Chemstrip bG , Dextrostix , and Visidex II home blood glucose
systems, drug may cause false decrease in mean glucose values.
False-positive results may occur in urinary 5-hydroxy-indoleacetic
acid test.
USES: This medication is used to treat mild to moderately
severe pain. Codeine phosphate is a narcotic pain reliever. It acts
on certain centers in the brain to give you pain relief.
Relation to other opiates
Codeine is the starting material and prototype of a large class of
mainly mild to moderately strong opioids such as hydrocodone,
dihydrocodeine and its derivatives such as nicocodeine. Other series
of codeine derivatives include isocodeine and its derivatives, which
were developed in Germany starting around 1920. Related to codeine
in other ways are Codeine-N-Oxide (Genocodeine), related to the
nitrogen morphine derivatives as is codeine methobromide, and
heterocodeine which is a drug six times stronger than morphine and
72 times stronger than codeine due to a small re-arrangement of the
molecule, viz. moving the methyl group from the 3 to the 6 position
on the morphine carbon skeleton. Drugs bearing resemblance to
codeine in effects due to close structural relationship are
variations on the methyl groups at the 3 position including
ethylmorphine a.k.a. codethyline (Dionine) and benzylmorphine (Peronine).
While having no narcotic effects of its own, the important opioid
precursor thebaine differs from codeine only slightly in structure.
Pseudocodeine and some other similar alkaloids not currently used in
medicine are found in trace amounts in opium as well.
Recreational use
Codeine can be used as a recreational drug. However, it has much
less abuse potential than some other opiates or opioids, such as
oxycodone and hydrocodone.
In some countries, cough syrups and tablets containing codeine are
available without prescription; some potential recreational users
are reported to buy codeine from multiple pharmacies so as not to
arouse suspicion. A heroin addict may use codeine to ward off the
effects of a withdrawal.
Codeine is also available in conjunction with the anti-nausea
medication promethazine in the form of a syrup. Brand named as
Phenergan with Codeine or generically as promethazine with codeine
this medication is quickly becoming one of the most highly abused
codeine preparations.
Codeine is also demethylated by reaction with pyridine to illicitly
synthesize morphine. Pyridine is toxic and possibly carcinogenic, so
morphine illicitly produced in this manner (and potentially
contaminated with pyridine) may be particularly harmful. Codeine can
also be turned into α-chlorodide which is used in the clandestine
synthesis of desomorphine (Permonid). Codeine can also be turned
directly into stronger derivatives of the dihydrocodeine and
hydrocodone families and a few others with various chemicals and
equipment.
 Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT. Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT.
Note /Government Notification:
These chemicals are designated as those that are used in the
manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to the
manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance) products
Import and Export *** subjected to your country government laws
/control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS).
MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many chemical
suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL Safety web site,
where this page was hosted, has been copied onto many other sites,
often without permission. If you have any doubts about the veracity
of the information that you are viewing, or have any queries, please
check the URL that your web browser displays for this page. If the
URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium Benzoate.htm/" the page is
maintained by the Safety Officer in Physical Chemistry at Oxford
University. If not, this page is a copy made by some other person
and we have no responsibility for it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive Drug
Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the federal
U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture, importation,
possession, use and distribution of certain substances is regulated.
The Act also served as the national implementing legislation for the
Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs.
|


|














