|

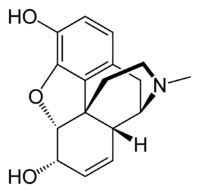
Morphine sulphate

Chemical data
Formula C17H19NO3
Mol. mass 285.34
Pharmacokinetic data
Bioavailability ~25% (oral); 100% (IV);
Protein binding 30–40%
Metabolism Hepatic 90%
Half life 2–3 h
Excretion Renal 90%, biliary 10%
DRUG DESCRIPTION
Morphine sulphate Cas No. 64-31-3
Morphine can be abused in a manner similar to other opioid agonists, legal
or illicit. This should be considered when prescribing or dispensing
Morphine sulphate in situations where the physician or pharmacist is
concerned about an increased risk of misuse, abuse, or diversion.
Chemically, morphine sulfate is
7,8-didehydro-4,5α-epoxy-17-methylmorphinan-3,6α-diol sulfate (2:1) (salt)
pentahydrate
Morphine sulphate Tablets are opiate analgesics supplied in 15, 30, 60, 100
and 200 mg tablet strengths. The tablet strengths describe the amount of
morphine per tablet as the pentahydrated sulfate salt (morphine sulfate, USP).
Morphine sulphate Controlled-release Tablets 15 mg, 30 mg, 60 mg, 100 mg,
and 200 mg contain the following inactive ingredients: cetostearyl alcohol,
hydroxyethyl cellulose, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene
glycol, talc and titanium dioxide.
DOSAGE
Morphine sulphate Cas No. 64-31-3
 The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Do
not increase your dose, take the medication more frequently, or take it for
a longer time than prescribed. Properly stop the medication when so
directed. You may also take quick-acting narcotic pain medications for
sudden (breakthrough) pain if so directed by your doctor. Also follow your
doctor's or pharmacist's instructions for safely using non-narcotic pain
relievers (such as naproxen, ibuprofen). If you have been using other
long-acting narcotic pain medications or narcotic patches regularly, check
with your doctor or pharmacist because you may need to stop using them
before you start using this medication. If you are currently using a
narcotic patch (such as fentanyl), the effects may continue after it is
removed. Ask your doctor or pharmacist when it will be safe to start taking
this medication (usually 18 hours after removing the patch). The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Do
not increase your dose, take the medication more frequently, or take it for
a longer time than prescribed. Properly stop the medication when so
directed. You may also take quick-acting narcotic pain medications for
sudden (breakthrough) pain if so directed by your doctor. Also follow your
doctor's or pharmacist's instructions for safely using non-narcotic pain
relievers (such as naproxen, ibuprofen). If you have been using other
long-acting narcotic pain medications or narcotic patches regularly, check
with your doctor or pharmacist because you may need to stop using them
before you start using this medication. If you are currently using a
narcotic patch (such as fentanyl), the effects may continue after it is
removed. Ask your doctor or pharmacist when it will be safe to start taking
this medication (usually 18 hours after removing the patch).
Take this medication by mouth with or without food, usually 2 or 3 times
daily (every 8 or 12 hours) or as directed by your doctor. If you have
nausea, it may help to take this drug with food. Consult your doctor or
pharmacist about other ways to decrease nausea (such as taking
antihistamines, lying down for 1 to 2 hours with as little head movement as
possible).
SIDE EFFECTS
Morphine sulphate Cas No. 64-31-3
The adverse reactions caused by morphine are essentially those observed with
other analgesics. They include the following major hazards:
respiratory depression, apnea, and to a lesser degree, circulatory
depression, respiratory arrest, shock, and cardiac arrest.
Most Frequently Observed
Constipation, lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, nausea, vomiting,
sweating, dysphoria, and euphoria.
Some of these effects seem to be more prominent in ambulatory patients and
in those not experiencing severe pain. Some adverse reactions in ambulatory
patients may be alleviated if the patient lies down.
Less Frequently Observed Reactions
Central Nervous System: Weakness, headache, agitation, tremor, uncoordinated
muscle movements, seizure, alterations of mood (nervousness, apprehension,
depression, floating feelings), dreams, muscle rigidity, transient
hallucinations and disorientation, visual disturbances, insomnia, increased
intracranial pressure
Gastrointestinal: Dry mouth, biliary tract spasm, laryngospasm, anorexia,
diarrhea, cramps, taste alteration, constipation, ileus, intestinal
obstruction, dyspepsia, increases in hepatic enzymes
Cardiovascular: Flushing of the face, chills, tachycardia, bradycardia,
palpitation, faintness, syncope, hypotension, hypertension
Genitourinary: Urine retention or hesitance, amenorrhea, reduced libido
and/or potency
Dermatologic: Pruritus, urticaria, other skin rashes, edema, diaphoresis
Other: Antidiuretic effect, paresthesia, bronchospasm, muscle tremor,
blurred vision, nystagmus, diplopia, miosis, anaphylaxis
PRECAUTIONS
Morphine sulphate Cas No. 64-31-3
Morphine sulphate Tablets are a controlled-release oral formulation of
morphine sulfate indicated for the management of moderate to severe pain
when a continuous, around-the-clock analgesic is needed for an extended
period of time. Morphine sulphate does not release morphine continuously
over the course of a dosing interval. The administration of single doses of
Morphine sulphate on a q12h dosing schedule will result in higher peak and
lower trough plasma levels than those that occur when an identical daily
dose of morphine is administered using conventional oral formulations on a
q4h regimen. The clinical significance of greater fluctuations in morphine
plasma level has not been systematically evaluated.
Selection of patients for treatment with Morphine sulphate® should be
governed by the same principles that apply to the use of morphine or other
potent opioid analgesics. Specifically, the increased risks associated with
its use in the following populations should be considered: the elderly or
debilitated and those with severe impairment of hepatic, pulmonary, or renal
function; myxedema or hypothyroidism; adrenocortical insufficiency (e.g.,
Addison's Disease); CNS depression or coma; toxic psychosis; prostatic
hypertrophy or urethral stricture; acute alcoholism; delirium tremens;
kyphoscoliosis or inability to swallow.
The administration of morphine, like all opioid analgesics, may obscure the
diagnosis or clinical course in patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Morphine may aggravate convulsions in patients with convulsive disorders,
and all opioids may induce or aggravate seizures in some clinical settings.
 |
|







 The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Do
not increase your dose, take the medication more frequently, or take it for
a longer time than prescribed. Properly stop the medication when so
directed. You may also take quick-acting narcotic pain medications for
sudden (breakthrough) pain if so directed by your doctor. Also follow your
doctor's or pharmacist's instructions for safely using non-narcotic pain
relievers (such as naproxen, ibuprofen). If you have been using other
long-acting narcotic pain medications or narcotic patches regularly, check
with your doctor or pharmacist because you may need to stop using them
before you start using this medication. If you are currently using a
narcotic patch (such as fentanyl), the effects may continue after it is
removed. Ask your doctor or pharmacist when it will be safe to start taking
this medication (usually 18 hours after removing the patch).
The dosage is based on your medical condition and response to treatment. Do
not increase your dose, take the medication more frequently, or take it for
a longer time than prescribed. Properly stop the medication when so
directed. You may also take quick-acting narcotic pain medications for
sudden (breakthrough) pain if so directed by your doctor. Also follow your
doctor's or pharmacist's instructions for safely using non-narcotic pain
relievers (such as naproxen, ibuprofen). If you have been using other
long-acting narcotic pain medications or narcotic patches regularly, check
with your doctor or pharmacist because you may need to stop using them
before you start using this medication. If you are currently using a
narcotic patch (such as fentanyl), the effects may continue after it is
removed. Ask your doctor or pharmacist when it will be safe to start taking
this medication (usually 18 hours after removing the patch).





