HOME >>
Chemicals
>> Benzene

|
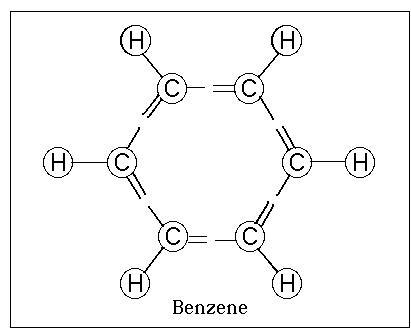
Benzene
|
|
CAS number : 71-43-2
Molecular formula : C6H6
Molar mass : 78.11 g mol−1
Appearance : Colorless liquid
Density : 0.8786 g/cm3
Melting point : 5.5 °C, 279 K, 42 °F
Boiling point : 80.1 °C, 353 K, 176 °F
Solubility in water : 0.8 g/L (25 °C)
Viscosity : 0.652 cP at 20 °C
Dipole moment : 0 D |
Benzene, or benzol, is an organic chemical compound
with the molecular formula C6H6. It is sometimes abbreviated Ph–H.
Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet
smell and a relatively high melting point. Because it is a known
carcinogen, its use as an additive in gasoline is now limited, but
it is an important industrial solvent and precursor in the
production of drugs, plastics, synthetic rubber, and dyes. Benzene
is a natural constituent of crude oil, and may be synthesized from
other compounds present in petroleum. Benzene is an aromatic
hydrocarbon and the second [n]-annulene ([6]-annulene), a cyclic
hydrocarbon with a continuous pi bond.
Production
Trace amounts of benzene may result whenever carbon-rich materials
undergo incomplete combustion. It is produced in volcanoes and
forest fires, and is also a component of cigarette smoke. Benzene is
a principal component of combustion products produced by the burning
of PVC (polyvinyl chloride).
Until World War II, most benzene was produced as a by-product of
coke production (or "coke-oven light oil") in the steel industry.
However, in the 1950s, increased demand for benzene, especially from
the growing plastics industry, necessitated the production of
benzene from petroleum. Today, most benzene comes from the
petrochemical industry, with only a small fraction being produced
from coal.
Four chemical processes contribute to industrial benzene production:
catalytic reforming, toluene hydrodealkylation, toluene
disproportionation, and steam cracking. In the US, 50% of benzene
comes from catalytic reforming and 25% from steam cracking. In
Western Europe, 50% of benzene comes from steam cracking and 25%
from catalytic reforming.
Uses
In the 19th and early-20th centuries, benzene was used as an
after-shave lotion because of its pleasant smell. Prior to the
1920s, benzene was frequently used as an industrial solvent,
especially for degreasing metal. As its toxicity became obvious,
benzene was supplanted by other solvents, especially toluene (methyl
benzene), which has similar physical properties but is not as
carcinogenic.
In 1903, Ludwig Roselius popularized the use of benzene to
decaffeinate coffee. This discovery led to the production of Sanka
(the letters "ka" in the brand name stand for kaffein). This process
was later discontinued. Benzene was historically found as a
significant component in many consumer products such as Liquid
Wrench, Testors model cement, several paint strippers, rubber
cements, spot removers and other hydrocarbon-containing products.
Some, like Testors, ceased manufacture of its benzene formula about
1950 while others continued to use benzene as a component or
significant contaminant until the late 1970s when leukemia deaths
were found associated with Goodyear's Pliofilm production operations
in Ohio. Until the late 1970s, many hardware stores, paint stores,
and other retail outlets sold benzene in small cans, such as quart
size, for general-purpose use. Many students were exposed to benzene
in school and university courses while performing laboratory
experiments with little or no ventilation in many cases. This very
dangerous practice has been almost totally eliminated.
As a gasoline (petrol) additive, benzene increases the octane rating
and reduces knocking. Consequently, gasoline often contained several
percent benzene before the 1950s, when tetraethyl lead replaced it
as the most widely-used antiknock additive. With the global phaseout
of leaded gasoline, benzene has made a comeback as a gasoline
additive in some nations. In the United States, concern over its
negative health effects and the possibility of benzene entering the
groundwater have led to stringent regulation of gasoline's benzene
content, with limits typically around 1%.
European petrol specifications now contain the same 1% limit on
benzene content. The United States Environmental Protection Agency
has new regulations that will lower the benzene content in gasoline
to 0.62% in 2011.
Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon that is produced by the burning
of natural products. It is a component of products derived from coal
and petroleum and is found in gasoline and other fuels. Benzene is
used in the manufacture of plastics, detergents, pesticides, and
other chemicals. Research has shown benzene to be a carcinogen
(cancer-causing). With exposures from less than five years to more
than 30 years, individuals have developed, and died from, leukemia.
Long-term exposure may affect bone marrow and blood production.
Short-term exposure to high levels of benzene can cause drowsiness,
dizziness, unconsciousness, and death.
 Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT. Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT.
Note /Government Notification: N/A

|

|


