HOME >>
Chemicals
>> Methylenedioxyphenyl-2-propanone

|
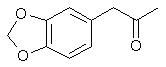
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl-2-propanone
|
|
IUPAC Name:
1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)propan-2-one
CAS Registry Number: 4676-39-5
Synonyms: Methyl piperonyl ketone,
5-Acetonyl-1,3-benzodioxole, 3,4-Methylenedioxyphenyl acetone,
3,4-Methylenedioxybenzyl methyl ketone,
1-(1,3-Benzodioxol-5-yl)acetone, CID78407, NSC16688, EINECS
225-128-6, 1-(Acetonyl)-3,4-methylenedioxybenzene, NSC 16688,
ZINC01747237, (3,4-(Methylenedioxy)phenyl)-2-propanone,
AI3-30059, 2-Propanone, 1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-, 2-Propanone,
(3,4-(methylenedioxy)phenyl)-, 2-Propanone, [3,4-(methylenedioxy)phenyl]-,
2-Propanone, 1-[3,4-(methylenedioxy)phenyl]-, 2-Propanone,
1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)- (9CI), 2-Propanone, 1-(3,4-(methylenedioxy)phenyl)-
(8CI), 4676-39-5
Molecular Formula: C10H10O3 Molecular
Weight: 178.184600 [g/mol]
H-Bond Donor: 0 H-Bond Acceptor: 3
Chemical Name: PIPERONYL METHYL KETONE |
3,4-methylenedioxy-phenyl-2-propanoneis a chemical
compound consisting of phenylacetone substituted with a
methylenedioxy functional group.
It is a chemical precursor of MDA, MDMA (more commonly known as
"Ecstasy" or "XTC"), MDEA and related chemicalsMDP2P is most
commonly synthesized by oxidizing the plant oil safrole or its
isomer isosafrole using the Wacker oxidation or peroxyacid
oxidation.
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-propanone (MDP-2-P or PMK) was prepared
by two different routes, i.e. by oxidizing isosafrole in an acid
medium and by 1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-nitropropene reduction.
The final product-MDP-2-P was subjected to GC/MS analysis.
The intermediates and reaction by-products were identified and the
‘route specific’ impurities were established.
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)butan-2-amine (MDP-2-MB, MBDB) is a new
homologue of N-methyl-1-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propan-2-amine (MDMA),
which is strictly controlled as a narcotic.
As part of our continuous survey on illegal designer drugs in the
Japanese market, we found that
N-methyl-4-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)butan-2-amine (MDP-3-MB, HMDMA)
was being sold as MBDB.
As this is the first time that HMDMA has been revealed to be in
market distribution, and its physico-chemical data is thus far
unreported, we describe the structure elucidation of HMDMA and
comparative analysis with related compounds.
The impurity profiles were obtained by means of GC/MS, some reaction
by-products were identified by means of the EI mass spectra
including low energy EI mass spectra and ‘route specific’ impurities
were established.
4-Methyl-5-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-[1,3]dioxolan-2-one
,N-methyl-2-methoxy-1-methyl-2-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-ethaneamine,3-methyl-6,7-methylenedioxyisoquinoline-1,4-dione
and N-cyclohexyloacetamide were found to be the synthesis markers of
greatest importance.
Abstract
This paper describes the structural elucidation of a compound
produced during the synthesis of
3,4-methylenedioxymethylamphet-amine (MDMA) via the reductive
amination of 3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl-2-propanone (3,4-MUP-2-P) with
methylamine and sodium cyanoborohydride. The compound was isolated
from MDMA by column chromatography, proton and carbon nuclear
magnetic resonance spectroscopy, LC/mass spectrometry, and total
synthesis were used to identify the compound as N-cyanomethyl-N-methyl-l-(3',4'-methylenedioxyphenyl)-2-propylamine.
This compound has been identified as a potential synthetic route
marker for the reductive amination of 3,4-MDP-2-P with methylamine
and sodium cyanoborohydride and as such it should prove valuable to
forensic scientists engaged in profiling illicit drugs. Profiling
MDMA can provide useful information to law enforcement agencies
relating to synthetic route, precursor chemicals and reagents
employed and may be used for comparative analyses of different drug
seizures.
This paper also describes the structural elucidation of the
analogous methylamphetamine synthetic route marker compound,
N-cyanomethyl-N-methyl-l-phenyl-2-propylamine, produced during the
reductive amination of phenyl-2-propanone using methylamine and
sodium cyanoborohydride.
Background
The investigation of clandestine drug manufacturing laboratories
represents a combined effort between the criminal investigator and
the forensic chemist. At an early point in an investigation the
special agent will frequently request a list of the chemicals and
synthesis methods used to produce a controlled substance. Providing
these lists is often a very simple assignment the forensic chemist.
A general understanding of various chemicals reactions and
techniques is a part of the forensic chemist's training, academic
background, and experience. Additionally, numerous specific and
detailed drug syntheses are also available to him from the open
literature. The chemist may, none the less, encounter problems when
reviewing published procedures. If the literature procedures do not
explicitly illustrate the synthesis of the desired pound, the
chemist may erroneously assume that it is not applicable to the
clandestine laboratory. This conclusion may, in part, be due to the
complicated nature of the procedure or to the apparent requirement
for specialized equipment. It may also arise from the failure of the
chemist to visualize an application of the literature to the
synthesis of the clandestine drug. In this context, the synthesis
methods are themselves clandestine; they are "hidden" within the
literature. A determined study of literature procedures, however,
often reveals that while they do not detail the synthesis of the
drug in question, they can be modified to give useful or simple
methods for its manufacture. Sometimes this requires only the
substitution of appropriate chemicals or certain changes in reaction
parameters or catalysts.
Examples of this conceptual approach can be shown by the synthesis
of the nonpsychoactive controlled substance phenyl-2-propanone
(P-2-P). Halting the clandestine manufacture of P-2-P is of
particular interest to enforcement personnel since it serves as the
primary precursor in a number of syntheses for amphetamine and
methamphetamine. By substitution of the chemicals and through slight
changes in procedure, two published syntheses have been modified for
P-2-P manufacture. These simple changes are illustrated below and
are of the type to be expected of a clandestine drug chemist. By
procuring chemicals and using procedures not generally recognized
for the production of the controlled substance, the clandestine
chemist may improve his chances to escape detection. Each of the two
procedures investigated give fair to excellent yields of P-2-P, and,
by using the procedures consecutively, yields are greatly increased.
Experimental
Procedure
The following procedure, which Tsuji et. al. [1] used for the
preparation of 1-decanone, required only the substitution of
allylbenzene (1-phenyl-2-propene) for 1- decene. A three-neck round
bottomed flask was fitted with a magnetic stirrer and a
pressure-equalized dropping funnel containing allylbenzene.
The flask was charged with a mixture of palladium chloride, cuprous
chloride, and aqueous N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). With all outlets
securely stoppered and wired down, an oxygen-filled balloon was
placed over one neck and the flask contents stirred at room
temperature to allow oxygen uptake. After a period of oxygenation,
allylbenzene was added dropwise. The solution was continuously
stirred under the pressurized balloon. During this period of
addition, the color of the solution turned from green to black and
gradually returned to green as the reaction approached completion.
The mixture was poured into cold hydrochloric acid and extracted
with methylene chloride (CH2Cl2). The extract was washed with
saturated sodium bicarbonate and dried over anhydrous sodium
sulfate. Through filtration and distillation, phenyl-2-propanone and
trans-beta-methylstyrene (1-phenyl-1-propene) were recovered.

 Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT. Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT.
Note /Government Notification: N/A

|

|


