HOME >>
Chemicals
>> Pseudoephedrine

|
Pseudoephedrine, its salts, optical isomers, and
salts of optical isomers
|
|
Identifiers
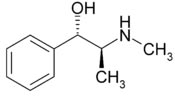
CAS number : 90-82-4
Formula : C10H15NO
Mol. Weight : 165.23
Melting Point:182 - 186 C
Solubility: Soluble (soluble in alcohol) RESIDUE Complies
Risk Codes:R20/21/22;R36/37/38 Details
Appearance:White fine powder
Synonyms: Isoephedrine, trans-Ephedrine, PSEUDOEPHEDRINE,
Sudafed, d-Pseudoephedrine, d-Isoephedrine, Psi-ephedrine,
Psi-ephedrin, d-psi-Ephedrine, Besan, (+)-Pseudoephedrine, L(+)-psi-Ephedrine,
(+)-threo-Ephedrine, (+)-psi-Ephedrine, L-(+)-Pseudoephedrine,
Pseudoephedrine (D), ()-psi-Ephedrine, ()-Pseudoephedrine, ( )-Pseudoephedrine,
Pseudoephedrine, (+)- |
 Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine commonly
used as a decongestant. The salts pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and
pseudoephedrine sulfate are found in many over-the-counter
preparations either as single-ingredient preparations, or more
commonly in combination with antihistamines, paracetamol
(acetaminophen) and/or ibuprofen. Sudafed is a trademark for a
common brand which contains pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, though
Sudafed PE does not. Cirrus contains pseudoephedrine in conjunction
with cetirizine (an antihistamine). Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine commonly
used as a decongestant. The salts pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and
pseudoephedrine sulfate are found in many over-the-counter
preparations either as single-ingredient preparations, or more
commonly in combination with antihistamines, paracetamol
(acetaminophen) and/or ibuprofen. Sudafed is a trademark for a
common brand which contains pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, though
Sudafed PE does not. Cirrus contains pseudoephedrine in conjunction
with cetirizine (an antihistamine).
Unlike antihistamines, which relieve multiple allergic symptoms by
acting as antagonists at histamine receptors, pseudoephedrine
primarily relieves nasal congestion commonly associated with colds
or allergies.
The advantage of oral pseudoephedrine over topical nasal
preparations, such as oxymetazoline, is that it does not cause
rebound congestion (rhinitis medicamentosa); however, it is more
likely to cause adverse effects including hypertension.
Pseudoephedrine is being phased out as an over-the-counter drug in
some countries and replaced by less effective alternative
decongestants such as phenylephrine, due to pseudoephedrine's use as
an ingredient in the manufacture of methamphetamine.
Pharmacokinetic data
Bioavailability unknown
Metabolism hepatic (10–30%)
Half life 9–16 hours
Excretion 70-90% renal
Pseudoephedrine is a decongestant that shrinks blood vessels in
the nasal passages. Dilated blood vessels can cause nasal congestion
(stuffy nose).
Pseudoephedrine is used to treat nasal and sinus congestion, or
congestion of the tubes that drain fluid from your inner ears,
called the eustachian (yoo-STAY-shun) tubes.
Important information about pseudoephedrine
Always ask a doctor before giving a cough or cold medicine to a
child. Death can occur from the misuse of cough and cold medicines
in very young children. Do not use any other over-the-counter cough
or cold medication without first asking your doctor or pharmacist.
If you take certain products together you may accidentally take too
much of a certain drug. Read the label of any other medicine you are
using to see if it contains pseudoephedrine. Do not use a cough or
cold medicine if you have used an MAO inhibitor such as
isocarboxazid (Marplan), phenelzine (Nardil), rasagiline (Azilect),
selegiline (Eldepryl, Emsam), or tranylcypromine (Parnate) within
the past 14 days. Serious, life-threatening side effects can occur
if you take cough or cold medicine before the MAO inhibitor has
cleared from your body.
Pseudoephedrineis a sympathomimetic amine commonly used as a
decongestant. The salts pseudoephedrine hydrochloride and
pseudoephedrine sulfate are found in many over-the-counter
preparations either as single-ingredient preparations, or more
commonly in combination with antihistamines, paracetamol
(acetaminophen) and/or ibuprofen. Sudafed is a trademark for a
common brand which contains pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, though
Sudafed PE does not. Cirrus contains Pseudoephedrine in conjunction
with Cetirizine (an antihistamine).The advantage of oral
pseudoephedrine over topical nasal preparations, such as
oxymetazoline, is that it does not cause rebound congestion
(rhinitis medicamentosa); however, it is more likely to cause
adverse effects including hypertension.
Clinical uses
Indications
Pseudoephedrine is indicated for the treatment of:
* nasal congestion
* sinus congestion
* Eustachian tube congestion.
Mechanism of action
Pseudoephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine—that is, its principal
mechanism of action relies on its indirect action on the adrenergic
receptor system. While it may have weak agonist activity at α- and
β-adrenergic receptors, the principal mechanism is to cause the
release of endogenous norepinephrine (noradrenaline) from storage
vesicles in presynaptic neurons. The displaced noradrenaline is
released into the neuronal synapse where it is free to activate the
aforementioned postsynaptic adrenergic receptors.
These adrenergic receptors are located on the muscles lining the
walls of blood vessels. When activated by pseudoephedrine, the
muscles contract, causing the blood vessels to constrict
(vasoconstriction). These constricted blood vessels now allow less
fluid to leave the blood vessels and enter the nose, throat and
sinus linings, which results in decreased inflammation of nasal
membranes as well as decreased mucus production. Thus, by
constriction of blood vessels, mainly those located in the nasal
passages, pseudoephedrine causes a decrease in the symptoms of nasal
congestion.
The vasoconstriction that pseudoephedrine produces is believed to be
principally an α-adrenergic receptor response. While all
sympathomimetic amines, to some extent, have decongestant action,
pseudoephedrine shows greater selectivity for the nasal mucosa and a
lower affinity for central nervous system (CNS) adrenergic-receptors
than other sympathomimetic amines.
Vasoconstriction in the nasal mucosa shrinks swollen nasal mucous
membranes, reduces tissue hyperemia, edema, and nasal congestion.
Other beneficial effects may include increasing the drainage of
sinus secretions, and opening of obstructed Eustachian tubes. The
same vasoconstriction action can also result in hypertension, which
is a noted side effect of pseudoephedrine.
Precautions and contraindications
It is recommended that pseudoephedrine not be used in patients with:
diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, prostatic
hypertrophy, hyperthyroidism, closed angle glaucoma and/or pregnancy
Since nasal congestion is considered to be a relatively minor
ailment, alternatives are preferred in patients with these
conditions. Appropriate alternatives may include topical
decongestants or saline sprays/instillations, depending on the
patient's condition.
Contraindications for the use of pseudoephedrine include:
concomitant or recent (previous fourteen days) monoamine oxidase
inhibitor (MAOI), or serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitor (SSRI)
therapy , severe or uncontrolled hypertension, and/or severe
coronary artery disease.
People with bipolar disorder should use care when taking
pseudoephedrine, as it can cause insomnia and thus trigger a manic
episode.
Chemistry
Pseudoephedrine is a phenethylamine, and a diastereomer of
ephedrine.Pseudoephedrine is the International Nonproprietary Name
(INN) of the (1S,2S)- diastereomer of ephedrine (which has 1R,2S-
configuration). Other names are (+)-pseudoephedrine and D-pseudoephedrine
 Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT. Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT.
Note /Government Notification: N/A

|


|


