HOME >>
Chemicals
>> Tyramine

|
Tyramine
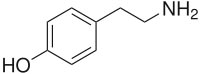
|
|
Identifiers
CAS number : 51-67-2
PubChem : 5610
MeSH Tyramine : C1=CC(=CC=C1CCN)O
Molecular formula : C8H11NO
Molar Weight : 137.179 g/mol |
Tyramineis a naturally-occurring monoamine
compound and trace amine derived from the amino acid
tyrosine.Tyramine acts as a catecholamine (dopamine, norepinephrine
(noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline)) releasing agent. Notably,
however, it is unable to cross the blood-brain-barrier (BBB),
resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic
effects. When ingested unintentionally from certain foods in
conjunction with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), tyramine is
responsible for the so-called "cheese effect" often seen with their
use.
Occurrence
Tyramine occurs widely in plants and animals and is metabolized by
the enzyme monoamine oxidase. In foods, it is often produced by the
decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay. Foods
containing considerable amounts of tyramine include meats that are
potentially spoiled or pickled, aged, smoked, fermented, or
marinated (some fish, poultry, and beef); most pork (except cured
ham); chocolate; alcoholic beverages; and fermented foods, such as
most cheeses (except ricotta, cottage cheese, cream cheese), sour
cream, yogurt, shrimp paste, soy sauce, soy bean condiments,
teriyaki sauce, tofu, tempeh, miso soup, sauerkraut; broad (fava)
beans, green bean pods, Italian flat (Romano) beans, Chinese (snow)
pea pods, avocados, bananas, pineapple, eggplants, figs, red plums,
raspberries, peanuts, Brazil nuts, coconuts, processed meat, yeast,
and an array of cacti.
Metabolism
In humans, if monoamine metabolism is compromised by the use of
monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and foods high in tyramine are
ingested, a hypertensive crisis can result as tyramine can cause the
release of stored monoamines, such as dopamine, norepinephrine,
epinephrine. The first signs of this were discovered by a
neurologist who noticed his wife, who at the time was on MAOI
medication, had severe headaches when eating cheese. For this
reason, the crisis is still called the "cheese syndrome," even
though other foods can cause the same problem.
Foods containing tyramine
This is a list of foods containing tyramine. Tyramine is an amine
which causes elevated blood pressure and tachycardia by displacing
norepinephrine from storage vesicles. Tyramine is generally produced
by decarboxylation of the amino acid tyrosine during fermentation of
food products. All protein-rich foods which have been matured will
contain more tyramine depending on the temperature and how long they
have been stored. Properly refrigerated foods will not be affected.
The amount required to cause a 30 mmHg (4.0 kPa) increase in
systolic blood pressure is referred to as TYR30, and generally
averages around 500 mg in an unmedicated, healthy individual. A
class of antidepressants called MAOIs (monoamine oxidase
inhibitors), and particularly MAOIs that inhibit the isozyme MAO-A,
can increase the sensitivity to tyramine if taken orally. If
sufficient quantities of tyramine are ingested after MAO-A
inhibition, hypertensive crises may occur, potentially causing
stroke or cardiac arrhythmia. There is significant evidence that
tyramine may trigger migraines in sensitive individuals.
This list is for informational purposes only; it is neither
all-inclusive nor does it go into any particular depth. If you plan
to avoid tyramine in your diet, you are urged to seek professional
guidance. Note that the exact increase in sensitivity will depend on
the MAOI used, and its dose.
* 1 Cheeses
* 2 Fruit
* 3 Processed foods
* 4 Meat and fish
* 5 Soy
* 6 Nuts and chocolate
Tyramine is a vaso-active amino acid found in foods. It precipitates
headaches in some sufferers. It is an intermediate product in the
conversion of tyrosine (an amino acid present in many proteins) to
epinephrine (an active hormone produced by the inner portion of the
adrenal gland).
Foods that contain tyramine may trigger headaches in migraineurs by
facilitating a chain reaction which results in selective cerebral
vasoconstriction followed by rebound dilation of the cranial vessels
(the most common cause of the throbbing headache pain). This
sequence of events is implicated in migraine headache.
Some of the foods containing tyramine are aged cheese, nuts,
herring, and chicken livers. A more complete diet listing is
available to members of the Foundation. Foods with high
concentration of tyramine are contraindicated with MAO1-type
antidepressants.
Antidepressant tyramine
Tyramine is know to interact with monoamine oxidase inhibitors
leading to dangerous effects. Tyramine is also thought to trigger
cluster headaches. Tyramine is ordinarily harmless. But for people
taking MAO inhibitor drugs such as the antidepressant medications
Nardil and Parnate, it poses a severe threat. When combined with
these drugs, it can cause a sudden, dangerous spike in blood
pressure.
 Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT. Note:
These API/ chemicals are designated as those that are used in
the manufacture of the controlled substances and are important to
the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control Substance)
products Import and Export *** subjected to your country government
laws /control substance ACT.
Note /Government Notification: N/A

|


|


