|
HOME >>
Chemicals
>>
Chemicals List 2 >> Methyl isobutyl ketone
Methyl isobutyl ketone
CAS number 108-10-1
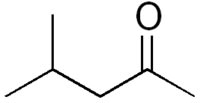
 Identifiers Identifiers
Synonyms: 4-methyl-2-pentanone, 4-methylpentan-2-one,
2-methyl-4-pentanone, 2-methylpropyl methyl ketone,
4-methyl-2-oxopentane, hexone, isopropylacetone, MIK, isobutylmethyl
ketone, MIBK, isohexanone
Use: artificial flavouring
Molecular formula: CH3COCH2CH(CH3)2
CAS No:108-10-1
Molecular Weight: 100.16
Physical data
Appearance: colourless liquid with a pleasant odour
Melting point: -85 C
Boiling point: 116 C
Vapour density: 3.5 (air = 1)
Vapour pressure: 15 mm Hg at 20 C
Density (g cm-3): 0.79
Flash point: 16 C (closed cup)
Explosion limits: 1.1 - 7.5 %
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility:
Stability Stable. Flammable - note low flash point. Incompatible
with strong oxidizing agents.
Toxicology
Harmful if inhaled. Eye, skin and respiratory irritant. Long-term or
repeated skin contact may cause dermatitis. Chronic high-level
exposure may lead to liver damage. Typical TLV/TWA 50 ppm. Typical
STEL 75 ppm.
Toxicity data
(The meaning of any toxicological abbreviations which appear in this
section is given here.)
ORL-RAT LD50 2080 mg kg-1
IHL-MUS LC50 23000 mg m-3
IPR-MUS LD50 268 mg kg-1
Risk phrases
R11 R20.
Personal protection
Safety glasses, adequate ventilation.
Description:
Methyl isobutyl ketone (C.A.S. 108-10-1) is a colorless liquid that
is used as a solvent for vinyl, epoxy, acrylic and natural resins,
nitrocellulose, paints, varnishes, lacquers, protective coatings,
rare metal extraction, and dyes.
It is used as a denaturant for rubbing alcohol, a synthetic
flavoring adjuvant, and a fruit flavoring.
It is used in extracting uranium from fission products, dewaxing
mineral oils, manufacturing antibiotics, dry-cleaning preparations,
and the synthesis of methyl isobutyl carbinol. It occurs naturally
in oranges, grapes, and vinegar.
Chemical properties:
Methyl isobutyl ketone has a faint ketonic and camphor odor. It is
classified under the Clean Air Act as a volatile organic compound.
It is moderately soluble in water, and soluble in alcohol, ether,
acetone, benzene, and chloroform.
It is miscible with most organic solvents. It is reactive or
incompatible with strong oxidizers, potassium, and tert-butoxide. It
is highly flammable and will be easily ignited by heat, sparks, or
flame.
Its vapors may form explosive mixtures with air and may travel to
the source of ignition and flash back.
The vapor may explode if ignited in an enclosed area. Most of its
vapors are heavier than air, and its liquids are lighter than water.
Methyl isobutyl ketone ignites on contact with potassium-t-butoxide.
It can react vigorously with reducing materials. Synonyms for methyl
isobutyl ketone include hexone, isobutyl methyl ketone,
4-methyl-2-pentanone, and isopropyl acetone.
Health effects:
Exposure to methyl isobutyl ketone may cause gastrointestinal
disturbances and central nervous system impairment, headache,
nausea, vomiting, and respiratory tract irritation.
Chronic exposure may cause axonal neuropathy, paresthesia, and
muscle weakness.
Ingestion of methyl isobutyl ketone may cause central nervous system
depression, respiratory depression, dyspnea, pulmonary aspiration,
and corrosive effects. Inhalation may cause coma, nausea, headache,
vertigo, incoordination, central nervous system depression,
narcosis, dizziness, tremors, cardiorespiratory failure, and eye,
nose, and throat irritation.
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 |



