|
HOME >>
Chemicals
>>
Chemicals List 1 >> Nitroethane
Nitroethane
CAS number 79-24-3
 General General
Synonyms:
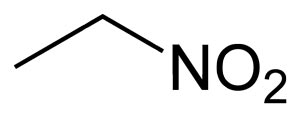
Molecular formula: C2H5NO2
CAS No: 79-24-3
EC No:
Physical data
Appearance: colourless oily liquid with an unpleasant odour
Melting point:
Boiling point: 114 C
Vapour density: 2.6 (air = 1)
Vapour pressure: 15.6 mm Hg at 20 C
Density (g cm-3): 1.05
Flash point: 31 C (closed cup)
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility: slight
Stability
Contact with a variety of materials may cause fire or explosion,
especially if heated. Incompatible with amines, strong acids, strong
oxidizing agents, combustible materials, metal oxides, strong bases,
alkalies.
Toxicology
Harmful if swallowed or inhaled. Typical TLV/TWA 100 ppm. Typical
STEL 150 ppm.
Toxicity data :
ORL-RBT LDLO 500 mg kg-1
IPR-MUS LD50 310 mg kg-1
Personal protection
Safety glasses, good ventilation. Do not heat.
Nitroethane is a chemical used mainly as in industrial solvent, fuel
additive, propellant, manufacture of pharmaceutical products and in
artificial nail removers .
Ingestion and other exposures to the chemical can cause various
symptoms. The type and severity of symptoms varies depending on the
amount of chemical involved and the nature of the exposure.
Nitroethane is an organic compound having the chemical formula
C2H5NO2. Similar in many regards to nitromethane, nitroethane is an
oily liquid at standard temperature and pressure.
Pure nitroethane is colourless and has a fruity odor. It is a high
volume chemical, with over 1 million pounds of nitroethane being
produced.
Nitroethane is produced industrially by treating propane with nitric
acid at 350–450 °C. This exothermic reaction produces four
industrially significant nitroalkanes: nitromethane, nitroethane,
1-nitropropane, and 2-nitropropane.
The reaction involves free radicals, such as CH3CH2CH2O., which
arise via homolysis of the corresponding nitrite ester. These alkoxy
radicals are susceptible to C-C fragmentation reactions, which
explains the formation of a mixture of products.
 Synonyms/Related: Synonyms/Related:
* Ethane, nitro-
* Nitroetan
* Nitroetan [Polish]
* Nitroethane
* Nitroethane [Flammable liquid]
Properties
Incompatiblities:
o amines
o combustible materials
o hydrocarbons
o metal oxides
o strong acids
o strong alkalis
o strong oxidizers
Health & Regulatory Guidelines
NFPA 704 Rating:
o Health Hazardard Rating
o Fire Hazardard Rating
o Reactivity Hazardard Rating
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 |