|
HOME >>
Chemicals
>>
Chemicals List 1 >> Piperonal
Piperonal
CAS number 120-57-0
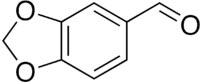
General
Synonyms: 3,4-(methylenedioxy)benzaldehyde,
1,3-benzodioxole-5-carboxaldehyde, heliotropin, heliotropine,
piperonaldehyde, protocatechuic aldehyde, piperonyl aldehyde
Molecular Weight: 150.131440 [g/mol]
H-Bond Donor: 0 H-Bond Acceptor: 3
Molecular formula: C8H6O3
CAS No: 120-57-0
EINECS No: 204-409-7
Physical data
Appearance: white crystalline solid
Melting point: 35 - 37 C
Boiling point: 264 C
Vapour density:
Vapour pressure:
Density (g cm-3):
Flash point: 113 C (closed cup)
Explosion limits:
Autoignition temperature:
Water solubility:
Stability
Stable, but air and light sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with
strong oxidizing agents, bases.
Toxicology
Skin irritant.
ORL-RAT LD50 2700 mg kg IPR-MUS LD50 480 mg kg Risk phrases R38 R52
R53.
Environmental information
Harmful to aquatic organisms - may cause long-term environmental
damage.
Personal protection
Safety glasses.
Piperonal
is an aromatic aldehyde that comes as transparent crystals, C8H6O3,
and has a floral odor. It is used as flavoring and in perfume. It
can be obtained by oxidation of piperonyl alcohol or piperic acid.
It is also a minor natural component of the extract of vanilla.
Piperonal's aroma is described as being similar to that of vanillin.
It finds use as a flavoring and in perfume. Piperonal has powerful
aromatherapeutic qualities which appear to elevate mood and general
well-being, and has shown in tests done by the Memorial
Sloan-Kettering Cancer
It may be used in the synthesis of 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA).
In one synthetic path, nitroethane in a glacial acetic acid solution
with an ammonium acetate catalyst yields a substituted nitrostyrene
via a condensation reaction.
Description
Piperonal is found in oils of Spirea ulmaria L., Doriphora sassafras
Endl., and other oils. It is prepared by oxidation of isosafrole. It
is a white crystalline substance with a sweet floral odour
resembling heliotrope and free from safrole by-odour.
PIPERONAL (heliotropine, protocatechuic aldehyde methylene ether),
C8H6O3
an aromatic aldehyde . It is prepared by oxidizing piperic See also:
 ACID
(from the Lat. root ac-, sharp; acere, to be sour) acid with See
also: POTASSIUM [symbol K (from kalium), atomic weight 39.114 0=16)]
potassium permanganate (R . See also: * FITTIG, RUDOLF (1835– )
Fittig, See also: ANN Ann., 1869, 152, p . 35); by condensing
methylene iodide with protocatechuic aldehyde (R . See also: *
WEGSCHEIDER, JULIUS AUGUST LUDWIG (1771-1849) Wegscheider, Monats.,
1893, 14, p . 388) ; or by oxidizing isosafrol with chromic acid .
It forms See also: LONG, GEORGE (1800-1879) LONG, JOHN DAVIS
(1838– ) long colourless crystals which melt at 370 C. and See also:
BOIL boil at 263° C . It has an agreeable See also: SMELL (connected
etymologically with " smoulder " and " smoke ") smell, resembling
that of See also: ACID
(from the Lat. root ac-, sharp; acere, to be sour) acid with See
also: POTASSIUM [symbol K (from kalium), atomic weight 39.114 0=16)]
potassium permanganate (R . See also: * FITTIG, RUDOLF (1835– )
Fittig, See also: ANN Ann., 1869, 152, p . 35); by condensing
methylene iodide with protocatechuic aldehyde (R . See also: *
WEGSCHEIDER, JULIUS AUGUST LUDWIG (1771-1849) Wegscheider, Monats.,
1893, 14, p . 388) ; or by oxidizing isosafrol with chromic acid .
It forms See also: LONG, GEORGE (1800-1879) LONG, JOHN DAVIS
(1838– ) long colourless crystals which melt at 370 C. and See also:
BOIL boil at 263° C . It has an agreeable See also: SMELL (connected
etymologically with " smoulder " and " smoke ") smell, resembling
that of See also:
HELIOTROPE HELIOTROPE, or TURNSOLE heliotrope, and is much
used in See also: PERFUMERY (Lat. per, through, and fumare, to
smoke) perfumery . It is only slightly soluble in See also:
COLD (in O. Eng. cald and ceald, a word coming ultimately from a
root cognate with the Lat. gelu, gelidus, and common in the Teutonic
languages, which usually have two distinct forms for the substantive
and the adjective, cf. Ger. Kolte, kalt, Dutch koude cold See also:
WATER water, but is readily soluble in See also: ALCOHOL
alcohol and in See also: ETHER, (C2H5)2O ether . When heated with
dilute hydrochloric acid to Zoo° C. it yields protocatechuic
aldehyde, C7H6O3, and See also: CARBON (symbol C, atomic weight 12)
carbon . It readily combines with See also: SODIUM [symbol Na,
from Lat. natrium; atomic weight 23.00 (0=16)] sodium bisulphite and
with various bases .
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 |



