|
HOME >>
Chemicals
>>
Chemicals List 1 >> Benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde
CAS number 100-52-7
 PRODUCT
IDENTIFICATION PRODUCT
IDENTIFICATION
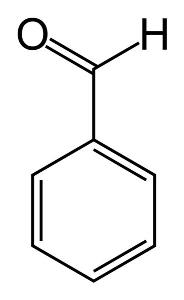
BENZALDEHYDE
EINECS NO. 202-860-4
FORMULA C6H5CHO
MOL WT. 106.12
H.S. CODE 2912.21
TOXICITY
Oral rat LD50: 1300 mg/kg
SYNONYMS Benzenecarboxaldehyde; Benzoic aldehyde;
Artificial Almond Oil; Benzenecarbonal; Phenylmethanal; Almond
artificial essential oil; Phenylmethanal benzenecarboxaldehyde;
Benzadehyde; Benzene carbaldehyde; Phenylmethanal;
DERIVATION CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
PHYSICAL STATE
Colourless to yellow liquid with bitter almonds odor
MELTING POINT -26 C
BOILING POINT 179 C
SPECIFIC GRAVITY 1.044
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
Soluble pH
VAPOR DENSITY
AUTOIGNITION 192 C
NFPA RATINGS Health: 2 Flammability: 2 Reactivity: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
1.5450
FLASH POINT
64 C
STABILITY Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Benzaldehyde(also called Benzenecarbonal) is the simplest
representative of the aromatic aldehydes. It is a colorless liquid
aldehyde with a characteristic almond odor. It boils at 180°C, is
soluble in ethanol, but is insoluble in water.
Benzaldehyde is formed by partial oxidation of benzyl alcohol and
readily oxidized to benzoic acid and is converted to addition
products by hydrocyanic acid or sodium bisulfite. It is also
prepared by oxidation of toluene or benzyl chloride or by treating
benzal chloride with an alkali, e.g., sodium hydroxide. It is used
chiefly in the synthesis of other organic compounds, ranging from
pharmaceuticals to plastic additives and benzaldehyde is an
important intermediate for the processing of perfume and flavouring
compounds and in the preparation of certain aniline dyes .
It is the first step in the synthesis for fragrances. It undergoes
simultaneous oxidation and reduction with alcoholic potassium
hydroxide, giving potassium benzoate and benzyl alcohol.
It is converted to benzoin with alcoholic potassium cyanide, with
anhydrous sodium acetate and acetic anhydride, giving cinnamic acid.
Compounds which do not have alpha-hydrogen atoms cannot form an
enolate ion and do not undergo electrophilic alpha-substitution and
aldol condensation.
Aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and formaldehyde may undergo
disproportionation in concentrated alkali (Cannizaro's reaction);
one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to the corresponding alcohol
and another molecule is simultaneously oxidized to the salt of a
carboxylic acid. The speed of the reaction depends on the
substituents in the aromatic ring. Two different types of aldehydes
(aromatic and aliphatic) can undergo crossing reaction to form
fomaldehyde and aromatic alcohols.
SALES SPECIFICATION
APPEARANCE
Clear to yellow liquid
ASSAY 99.0% min
TOLUENE 0.1% max
CHLORINE 20ppm max
ACIDITY 0.5% max (as Benzoic Acid)
BOILING POINT 177-182 C
RELATIVE DENSITY 1.041 - 1.043 at 20 C
Stability
Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents,
strong acids, reducing agents, steam. Air, light and
moisture-sensitive.
Toxicity data
(The meaning of any abbreviations which appear in this section is
given here.)
ORL-RAT LD50 1300 mg kg-1
SCU-RAT LDLO 5000 mg kg-1
SCU-RBT LD50 5000 mg kg-1
ORL-GPG LD50 1000 mg kg-1
| |
|
Note /Government
Notification: These chemicals are designated as those that are
used in the manufacture of the controlled substances and are
important to the manufacture of the substances. For any (Control
Substance) products Import and Export *** subjected to your
country government laws /control substance ACT.
Information: The information on this web page is provided to
help you to work safely, but it is intended to be an overview of
hazards, not a replacement for a full Material Safety Data Sheet
(MSDS). MSDS forms can be downloaded from the web sites of many
chemical suppliers. ,also that the information on the PTCL
Safety web site, where this page was hosted, has been copied
onto many other sites, often without permission. If you have any
doubts about the veracity of the information that you are
viewing, or have any queries, please check the URL that your web
browser displays for this page. If the URL begins "www.tajapi.com/www/Denatonium
Benzoate.htm/" the page is maintained by the Safety Officer in
Physical Chemistry at Oxford University. If not, this page is a
copy made by some other person and we have no responsibility for
it.
The Controlled Substances Act (CSA) was enacted into law by the
Congress of the United States as Title II of the Comprehensive
Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act of 1970.[1] The CSA is the
federal U.S. drug policy under which the manufacture,
importation, possession, use and distribution of certain
substances is regulated. The Act also served as the national
implementing legislation for the Single Convention on Narcotic
Drugs |
|
|
 New Chemicals New Chemicals
Phenyl acetic acid,
3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl-2-propanone,
Piperidine and its salts,
Methylamine,
Propionic anhydride,
Para Methoxy Phenyl Acetone,Para Methoxy Phenyl Acetic Acid,
Benzene,
Benzyl methyl ketone,
3'-Aminoacetophenone,
Ethylamine,
Isosafrole,
Piperonal,
N-methylpseudoephedrine
|



